SeparableSum¶
- class odl.solvers.functional.default_functionals.SeparableSum(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
FunctionalThe functional corresponding to separable sum of functionals.
The separable sum of functionals
f_1, f_2, ..., f_nis given byh(x_1, x_2, ..., x_n) = sum_i^n f_i(x_i)
The separable sum is thus defined for any collection of functionals with the same range.
Notes
The separable sum of functionals
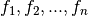 is given by
is given by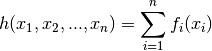
It has several useful features that also distribute. For example, the gradient is a
DiagonalOperator: =
[\nabla f_1(x_i), \nabla f_2(x_i), ..., \nabla f_n(x_i)]](../_images/math/0560d1bfa5ffe5f58659d71e661f8ae035672c6e.png)
The convex conjugate is also a separable sum:
 = \sum_{i=1}^n f_i^*(y_i)](../_images/math/bb4815fc19ed30a77b122a9d26c2eb8e611cff42.png)
And the proximal distributes:
![\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma h}(x_1, x_2, ..., x_n) =
[\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma f_1}(x_1),
\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma f_2}(x_2),
...,
\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma f_n}(x_n)].](../_images/math/b33851743065bce0cf70534490f48933a0fe26e6.png)
If
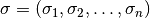 is a list
of positive
is a list
of positive float's, then it distributes, too:![\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma h}(x_1, x_2, ..., x_n) =
[\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma_1 f_1}(x_1),
\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma_2 f_2}(x_2),
...,
\mathrm{prox}_{\sigma_n f_n}(x_n)].](../_images/math/922ad8659d3c74ada8da71ee153f565c604ee46c.png)
- Attributes:
adjointAdjoint of this operator (abstract).
convex_conjThe convex conjugate functional.
domainSet of objects on which this operator can be evaluated.
functionalsThe summands of the functional.
grad_lipschitzLipschitz constant for the gradient of the functional.
gradientGradient operator of the functional.
inverseReturn the operator inverse.
is_functionalTrueif this operator's range is aField.is_linearTrueif this operator is linear.proximalReturn the
proximal factoryof the functional.rangeSet in which the result of an evaluation of this operator lies.
Methods
__call__(x[, out])Return
self(x[, out, **kwargs]).bregman(point, subgrad)Return the Bregman distance functional.
derivative(point)Return the derivative operator in the given point.
norm([estimate])Return the operator norm of this operator.
translated(shift)Return a translation of the functional.
- __init__(*functionals)[source]¶
Initialize a new instance.
- Parameters:
- functional1, ..., functionalN
Functional The functionals in the sum. Can also be given as
space, nwithninteger, in which case the functional is repeatedntimes.
- functional1, ..., functionalN
Examples
Create functional
f([x1, x2]) = ||x1||_1 + ||x2||_2:>>> space = odl.rn(3) >>> l1 = odl.solvers.L1Norm(space) >>> l2 = odl.solvers.L2Norm(space) >>> f_sum = odl.solvers.SeparableSum(l1, l2)
The
proximalfactory allows using vector-valued stepsizes:>>> x = f_sum.domain.one() >>> f_sum.proximal([0.5, 2.0])(x) ProductSpace(rn(3), 2).element([ [ 0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [ 0., 0., 0.] ])
Create functional
f([x1, ... ,xn]) = \sum_i ||xi||_1:>>> f_sum = odl.solvers.SeparableSum(l1, 5)